Page 177 - Class 10th Biology Chapter " Control and Coordination" NCERT Book Questions and Answers
| Chapter - " Control and Coordination" |
|---|
Page 119
Question 1:
What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer :
≻ A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not
involve any thinking. For example, we close our eyes immediately when
the bright light is focused.
≻ Walking, on the other hand, is a voluntary action. It is under our conscious
control.
Question 2:
What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer :
A very small gap that occurs between the last portion of axon of one neuron and
the dendrite of the other neuron is known as a synapse. It acts as a one way valve
to transmit impulses in one direction only.
This one-directional transfer of impulses occurs as the chemicals are produced in
only one side of the neuron i.e., the axon’s side. From axon, the impulses travel
across the synapse to the dendrite of the other neuron.
Question 3:
Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer :
Cerebellum, a part of hindbrain is responsible for maintaining posture and
equilibrium of the body.
Question 4:
How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer :
The thinking part of our brain is the forebrain. It has separate areas that are
specialized for hearing, smelling, sight, taste, touch, etc. The forebrain also has
regions that collect information or impulses from the various receptors. When the
smell of an incense stick reaches us, our forebrain detects it. Then, the forebrain
interprets it by putting it together with the information received from other
receptors and also with the information already stored in the brain.
Question 5:
What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer :
Reflex actions are sudden responses, which do not involve any thinking. For
example, when we touch a hot object, we withdraw our hand immediately without
thinking as thinking may take time which would be enough to get us burnt. The
sensory nerves that detect the heat are connected to the nerves that move the
muscles of the hand. Such a connection of detecting the signal from the nerves
(input) and responding to it quickly (output) is called a reflex arc. The reflex arcs
–connections present between the input and output nerves − meet in a bundle in
the spinal cord.
Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord and the information (input) reaches the
brain. The brain is only aware of the signal and the response that has taken place.
However, the brain has no role to play in the creation of the response.
Page 122
Question 1:
What are plant hormones?
Answer :
Plant hormones or phytohormones arenaturally-occurring organic substances.
These are synthesized in one part of the plant body (in minute quantities) and are
translocated to other parts when required. The five major types of phytohormones
are auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid and ethylene.
≻ Gibberellins help in the growth of the stem.
≻ Auxins help in the growth of the stem.
≻ Cytokinins promote cell division.
≻ Abscisic acid is one example of a hormone which inhibits growth.
Question 2:
How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement
of a shoot towards light?
Answer :
≻ The movement of leaves of the sensitive plant, Mimosa pudica or “touch
me not”, occurs in response to touch or contact stimuli. This is done by
plant cells by changing the amount of water in leaves. This movement is
independent of growth.
≻ The movement of shoot towards light is known as phototropism. This type
of movement is directional and is growth dependent.
Question 3:
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer :
Examples of plants growth hormones:
≻ Gibberellins help in the growth of the stem.
≻ Auxins help in the growth of the stem.
≻ Cytokinins promote cell division.
Question 4:
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer :
These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support,
auxin (a growth hormone) diffuses from the part of the tendril in contact with the
object to other side, which is not in the contact. Therefore the part of the tendril
in the contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril
away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus
cling to it.
Question 5:
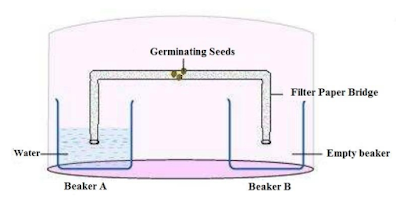
Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer :
Take two small beakers and label them as A and B. Fill beaker A with water. Now
make a cylindrical-shaped roll from a filter paper and keep it as a bridge between
beaker A and beaker B, as shown in the figure. Attach few germinating seeds in
the middle of the filter paper bridge. Now, cover the entire set-up with a
transparent plastic container so that the moisture is retained.
Observation:
The roots of the germinating seeds will grow towards beaker A.
This experiment demonstrates the phenomenon of hydrotropism
Page 125
Question 1:
How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer :
Chemical coordination takes place in animals with the help of hormones.
Hormone is the chemical messenger that regulates the physiological processes in
living organisms. It is secreted by glands. The regulation of physiological
processes and control and coordination by hormones comes under the endocrine
system. The nervous system along with the endocrine system in our body controls
and coordinates the physiological processes.
Question 2:
Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer :
Iodine stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxin hormone. It regulates
carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism in our body. Deficiency of this
hormone results in the enlargement of the thyroid gland. This can lead to goitre,
a disease characterized by swollen neck. Therefore, iodised salt is advised for
normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
Question 3:
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer :
Adrenalin is a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands in case of any danger or
emergency or any kinds of stress. It is secreted directly into the blood and is
transported to different parts of the body.
When secreted in large amounts, it speeds up the heartbeat and hence supplies
more oxygen to the muscles. The breathing rate also increases due to contractions
of diaphragm and rib muscles. It also increases the blood pressure. All these
responses enable the body to deal with any stress or emergency.
Question 4:
Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer :
Diabetes is a disease in which the level of sugar in the blood is too high. Insulin,
a hormone secreted by the pancreas, helps in regulating the blood sugar levels.
This is the reason why diabetic patients are treated by giving injections of insulin.
Exercises
Question 1:
Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin.
Answer :
(d) Cytokinin is a plant hormone.
Question 2:
The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite.
(b) synapse.
(c) axon.
(d) impulse.
Answer :
(b) The gap between two neurons is called a synapse.
Question 3:
The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking.
(b) regulating the heart beat.
(c) balancing the body.
(d) all of the above.
Answer :
(d) The brain is responsible for thinking, regulating the heart beat and balancing
the body.
Question 4:
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors
do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer :
Receptors are sensory structures (organs/tissues or cells) present all over the
body. The receptors are either grouped in case of eye or ear, or scattered in case
of skin.
Functions of receptors:
≻ They sense the external stimuli such as heat or pain.
≻ They also trigger an impulse in the sensory neuron which sends message
to the spinal cord.
When the receptors are damaged, the external stimuli transferring signals to the
brain are not felt. For example, in the case of damaged receptors, if we
accidentally touch any hot object, then our hands might get burnt as damaged
receptors cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
Question 5:
Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Answer :
Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system. The three main parts of a
neuron are axon, dendrite and cell body.
Functions of the three parts of a neuron:
≻ Axon: It conducts messages away from the cell body.
≻ Dendrite: It receives information from axon of another cell and conducts
the messages towards the cell body.
≻ Cell body: It contains nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles. It is
mainly concerned with the maintenance and growth.
Question 6:
How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer :
The movement of plant in response to light is called phototropism. Stem shows
positive phototropism as follows:
When growing plants detect light, a hormone called auxin, synthesised at the
shoot tip, helps the cells to grow longer. When light is coming from one side of
the plant, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration
of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away
from light. Thus, the plant appears to bend towards light.
Question 7:
Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer :
The reflex arc connections between the input and output nerves meet in a bundle
in the spinal cord. In fact, nerves from all over the body meet in a bundle in the
spinal cord on their way to the brain. In case of any injury to the spinal cord, the
signals coming from the nerves as well as the signals coming to the receptors will
be disrupted.
Question 8:
How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer :
Animals have a nervous system for controlling and coordinating the activities of
the body. But plants have neither a nervous system nor muscles.
Plants respond to stimuli by showing movements. The growth, development, and
responses to the environment in plants is controlled and coordinated by a special
class of chemical substances known as hormones. These hormones are produced
in one part of the plant body and are translocated to other needy parts. For
example, a hormone produced in roots is translocated to other parts when
required. The five major types of phytohormone are auxins, gibberellins,
cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene. These phytohormones are either growth
promoters (such as auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, and ethylene) or growth
inhibitors such as abscisic acid.
Question 9:
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Answer :
The maintenance of the body functions in response to changes in the body by
working together of various integrated body systems is known as coordination.
All the movements that occur in response to stimuli are carefully coordinated and
controlled. In animals, the control and coordination movements are provided by
nervous and muscular systems. The nervous system sends messages to and away
from the brain. The spinal cord plays an important role in the relay of messages.
In the absence of this system of control and coordination, our body will not be
able to function properly.
For example, when we accidentally touch a hot utensil, we immediately withdraw
our hand. In the absence of nerve transmission, we will not withdraw our hand
and may get burnt.
Question 10:
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer :
Involuntary actions cannot be consciously controlled. For example, we cannot
consciously control the movement of food in the alimentary canal or pumping of
blood through heart. These actions are however directly under the control of the
brain. On the other hand, the reflex actions such as closing of eyes immediately
when bright light is focused show sudden response and do not involve any
thinking. This means that unlike involuntary actions, the reflex actions are not
under the control of brain.
Question 11:
Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and
coordination in animals.
Answer :
| Nervous system mechanism | Hormonal system mechanism |
|---|---|
1. The information is conveyed in the form of electric impulse. 2. The axons and dendrites transmit the information through a coordinated effort. 3. The flow of information is rapid and the response is quick. 4. Its effects are short lived. |
1. The information is conveyed in the form of chemical messengers. 2. The information is transmitted or transported through blood. 3. The information travels slowly and the response is slow. 4. It has prolonged effects. |
Question 12:
What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a
sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer :
| Movement in sensitive plants | Movement in our legs |
|---|---|
1. The movement that takes place in a sensitive plant such as Mimosa pudica occurs in response to touch (stimulus). 2. For this movement, the information is transmitted from cell to cell by electrochemical signals as plants do not have any specialised tissue for conduction of impulses. 3. For this movement to occur, the plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them. |
1. Movement in our legs is an example of voluntary actions. 2. The signal or messages for these actions are passed to the brain and hence are consciously controlled. 3. In animal muscle cells, some proteins are found which allow the movement to occur. |
------