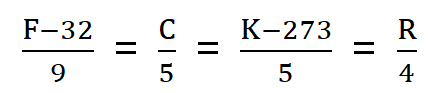Page 104 - Class 9th Chemistry Chapter Matter around us note
Chapter - Matter around us
• Matter /Substance :- Matter is called that which has weight, which occupies space and whose existence can be detected by sense organs.
For example :- Fe, Br, NaCl, CaCo3
# There are two types of substances -
1. Pure Matter
2. Impure Matter
For example :- Fe, Br, NaCl, CaCo3
# There are two types of substances -
1. Pure Matter
2. Impure Matter
1. Pure Matter:- Such a substance which is made up of only one type of particles or only one type of atoms or molecules, is called a pure substance.
For example :- Fe , Br , NaCl , CaCo3, MgSO4
2. Impure substance: - Such a substance which is made up of different types of particles or atoms or molecules is called an impure substance.
Eg:- air, sea water, mixture, soil
# There are two types of pure substances -
1. Element
2. compound
1. Element :- Element is called that substance which cannot be broken into two or more substances by any chemical or physical method.
For example :- Au , Ag , Cu , P , S , O , N
2. Compound: - A compound is a substance which is formed by chemical combination of two or more elements in a definite proportion and those elements cannot be separated by physical method.
Eg :- H2O , NaCl , Na2CO3
# There are three types of Elements -
1. Metal
2. Non-Metal
3. Metalloid
1. Metal
2. Non-Metal
3. Metalloid
1. Metal:- Metal is that element which has a special kind of luster, which is a good conductor of heat and electricity, which can be beaten into wire or sheet and which emits a special kind of sound when beaten.
For Example :- Au, Ag, Cu, Fe etc
Note :- Pb is a metal which is a bad conductor of electricity.
2. Non-metal: - Non-metal is called that element which does not have a special type of shine, which is a bad conductor of heat and electricity, which cannot be made into wire or sheet by beating and which does not make a special type of sound when beaten.
For Example :- C , P , S , O , N , Br
Note :- Graphite is such a nonmetal which is a good conductor of electricity.
3. Sub-metals/Metalloid :- Such elements which react both as metals and non-metals are called sub-metals.
For example: Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Silicon (Si), Tellurium (Te), Palonium (Po).
• What is a mixture?
Answer :- A mixture is a substance which is made up of mixing two or more substances in an indefinite proportion.
Example: - Mixture of sugar and water
Note :- 1. The properties of the constituent substances in the mixture are present.
2. The constituent substances of a mixture can be separated by simple physical or mechanical methods.
# There are two types of Mixture
(i) Homogeneous Mixture
(ii) Heterogeneous Mixture
(i) Homogeneous Mixture:- Such a mixture in which the properties and composition of each part are same, it is called homogeneous mixture.
For example: - Mixture of sugar and water
(ii) Heterogeneous Mixture:- Such a mixture in which the properties and composition of each part are not same, it is called heterogeneous mixture.
For example: - Mixture of salt and sugar
• What is inert gas?
Answer:- Such gases which do not react with any substance are called inert gases.
For example: - Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe), Radan (Rn)
• What is Atom?
Answer :- The smallest piece of an element is called an atom. Which does not remain in free state and can participate in any chemical reaction.
For example: O, an atom of oxygen.
Mg, an atom of magnesium.
Note :- The symbol of an element is denoted by one of its atoms.
•What is a molecule?
Answer :- The smallest piece of a compound is called a molecule. A molecule remains in a free state and has all the properties of that compound. If the molecule is broken again, it is different from its first properties.
or
When two or more atoms join together through chemical bonds, they form a molecule. A molecule is the smallest particle that can exist independently and shows chemical properties. When a molecule is formed, a new substance may be formed, which is different from the original atoms.
E.g.:- H2O(one molecule of water)
NaCl(one molecule of common salt)
Note: The formula of a compound represents one molecule of it.
•Nucleus:- The atom of any element is spherical and its total mass is present at its centre, that centre is called the nucleus of that atom.
•Nucleus:- The atom of any element is spherical and its total mass is present at its centre, that centre is called the nucleus of that atom.
Fundamental Properties of an Atom
An atom has three fundamental properties.
(i) Proton
(ii) Electron
(iii) Neutron
(i) Proton:- Proton resides in the nucleus of the atom. It has a positive electric charge. Its mass is equal to the mass of 1 hydrogen atom.
(ii) Electron:- Electron resides in the orbit of the atom. It has a triple electric charge. Its mass is equal to 1/1837th of the mass of 1 hydrogen atom. Which is considered to be zero.
(iii) Neutron:- Neutron resides in the nucleus of the atom. It has no electric charge. Its mass is equal to the mass of 1 hydrogen atom.
Note:- The mass of a neutron is slightly more than the mass of a proton.
•Volume:- The amount of space an object occupies is called the volume of that object.
Volume is represented by “V”.
Its SI unit is cubic meter.
•Area:- The amount of surface present inside a substance is called the area of that substance.
It is represented by ar.
Its SI unit is square meter.
•Shape:- The geometrical form of a substance is called the shape of that substance.
•Density:- The mass of a unit volume of a substance is called the density of that substance.
Density = Mass / Volume
Its SI unit is kilogram / cubic meter.
•Compressibility:- The process of increasing the density of a substance by applying force on it is called compressibility.
Or
The process of reducing the distance between the particles of a substance by applying force on it is called compressibility.
•Heat:- Heat is a type of energy that moves from one object to another. It increases the speed of the molecule.
•Temperature:- The thermal state of an object is called temperature. It tells us that if that object is brought in contact with another object, it will give or take heat to the other object.
•Heat:- Heat is a type of energy that moves from one object to another. It increases the speed of the molecule.
Its SI unit is Joule.
Its CGS unit is Calorie.
1cal. = 4.2j
1cal. = 4.18j
1j = 0.24cal
1cal. = 4.18j
1j = 0.24cal
•Temperature:- The thermal state of an object is called temperature. It tells us that if that object is brought in contact with another object, it will give or take heat to the other object.
Its SI unit is Kelvin.
Its CGS unit is Celsius.
Its FPS unit is Degree Farenheit.
Relation in Degree Celsius, Degree Fahrenheit, Kelvin, Rivmer
• Absolute Zero:- At -273 degrees Celsius the volume of all gases becomes zero. This temperature is called absolute zero.
• Absolute temperature:- The temperature measured by considering -273 degrees Celsius as zero is called absolute temperature.
• Melting / Fusion:- The process of a solid substance becoming liquid after being heated is called fusion.
• Boiling:- The process of a liquid being heated and rapidly becoming vapor from every point of it at a certain temperature is called boiling.
• Evaporation:- The process of slowly forming vapor from the surface of a liquid at every temperature is called evaporation.
• Freezing:- The process of a substance which remains in liquid state at normal temperature, freezing after cooling is called freezing.
• Solidification:- The process of a substance which is in solid state at normal temperature, its liquid getting cooled and becoming solid is called solidification.
• Melting point:- The temperature at which a solid substance becomes liquid at normal pressure is called the melting point of that solid substance.
Note: The melting point of ice is 0 degree Celsius.
• Boiling point:- The temperature at which a liquid substance becomes gas at normal pressure is called the boiling point of that liquid substance.
Note: The boiling point of water is 100 degree Celsius.
• Diffusion:- The process by which the particles of a substance automatically mix with the particles of another substance and move from one place to another is called diffusion.
For example: If an incense stick is lit in a corner of a room, its fragrance automatically reaches other places through diffusion.
For example: If an incense stick is lit in a corner of a room, its fragrance automatically reaches other places through diffusion.
Note: The process of diffusion is the least in solids and the most in gases.
Considering the unit of temperature, thermometers are of the following types.
[1] Celsius thermometer – Marked from 0 °C to 100 °C.
[2] Fahrenheit thermometer – Marked from 32 °F to 212 °F.
[3] Kelvin thermometer – Marked from 273 °C to 373 °C.
[4] Kelvin thermometer – Marked from 0 °C to 80 °C.
[5] Clinical thermometer – Marked from 94 °F to 110 °F.
• Intermolecular space:- The space between two particles of matter is called intermolecular space.
• Intermolecular force:- The force of attraction between two particles of matter is called intermolecular force.
There are three states of matter based on its physical properties.
[1] Solid
[2] Liquid
[3] Gas
• Solid:- A substance whose volume and shape are both definite is called solid.
In a solid, the intermolecular force is more while the intermolecular space is less.
For example: iron ball, stone, brick, book
• Liquid:- A substance whose volume is definite but shape is not definite is called liquid.
Intermolecular force in a liquid is less than that in a solid while the intermolecular space is more.
For example: water, milk, oil, alcohol
• Gas:- A substance whose volume and shape are both indefinite is called gas.
Intermolecular force in a gas is less while the intermolecular space is more.
For example: air, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen
Apart from these three states of matter, there are two other states also
[4] Plasma State
[5] BEC State – Bose Einstien Condensate State
• Plasma State:- The state of matter in which the particles are more energetic and more excited. These particles are in the form of ionized gas.
• BEC State:- This state is achieved by cooling a gas having a density of 1 lakhth of the density of normal air to 2x10^-7 Kelvin.