Page 101 - Light
Light :- Reflection of light
• Light :- Light is a form of energy, which enables us to see an object.
Note:-
(i) Light is an electromagnetic wave.
(ii) Light always travels in a straight line.
• Ray of Light: - The straight line path of light traveling in any direction is called a ray of light.
• Beam of Rays :- A group of rays of light in a certain direction is called a beam.
There are three types of beams -
1. Parallel Beam of Rays
2. Convergent Beam of Rays
3. Divergent Beam of Rays
1. Parallel beam: - Such a beam in which all the rays are parallel to each other is called a parallel beam.
2. Converging beam: - Such a beam in which all the rays meet at a point is called a convergent beam.
3. Diverging beam: - Such a beam in which all the rays appear to be scattered from a single point is called a diverging beam.
• Shadow:- When an opaque object is placed on the path of light, the light does not pass through that opaque object, so a dark area is formed there which is called shadow.
• Mirror :- That piece of a substance is called a mirror which is a relief surrounded by two surfaces. Out of which one surface remains clean and the other remains polished.
There are two types of mirrors
1. Plane Mirror
2. Spherical Mirror
1. Plane mirror: - That mirror is called a plane mirror, both the surfaces of which are flat, out of which one surface is polished.
2. Spherical mirrors: - Spherical mirrors are called that which is a section of a hollow sphere, in which one of the two surfaces that are pressed down or raised up remains clean and the other is polished.
**
There are two types of Spherical mirrors.
1. Concave Mirror
2. Convex Mirror
1. Concave mirror:- Such a spherical mirror in which light is reflected from the surface pressed down, it is called concave mirror.
2. Convex mirror: - Such a spherical mirror in which light is reflected from the raised surface is called a convex mirror.
# Reflection of light in a plane mirror

2. Incident ray: - The ray of light which is reflected on the mirror is called incident ray.
3. Reflected ray: - The ray of light which is returning after colliding with the mirror is called reflected ray.
4. Normal :- The normal drawn at the point of incidence of a mirror is called the normal of that mirror.
5. Angle of incidence :- The angle formed by the incident ray and the normal at the point of incidence is called the angle of incidence.
6. Reflected angle: - The angle formed by the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence is called the reflected angle.
1. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all fall in the same plane.
2. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
***
• What is image?
Answer :- The point at which the rays of light coming from an object point intersect or appear to intersect after being reflected or refracted is called the image of that object.
(i) Real Image:- Such an image which is formed by the actual meeting of reflected or refracted rays is called real image.

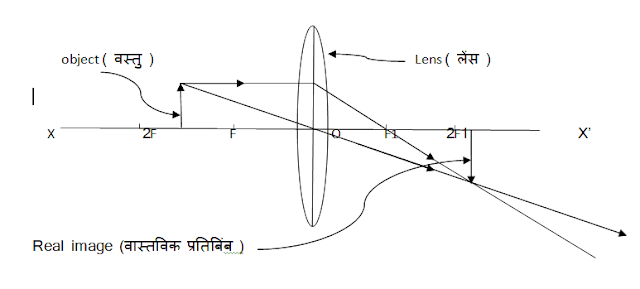
(ii) Imaginary Image / Virtual Image :- Such an image which is formed by virtual intersection of reflected or refracted rays is called imaginary image.
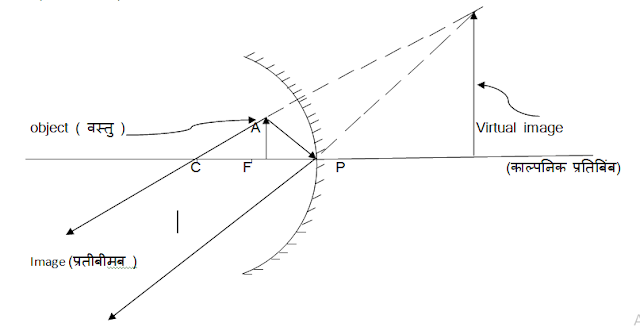
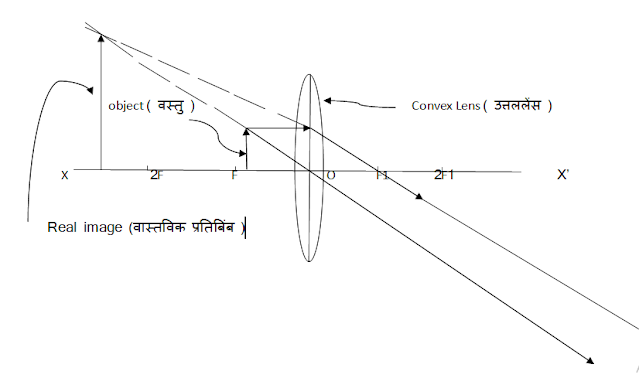
# Difference between imaginary and real image
| Virtual Image | Real Image |
|---|---|
| 1. This image is formed by the virtual intersection of the reflected or refracted rays. 2.This image is always erect. 3. This image cannot be shown on the screen. 4. It formed back on the mirror. 5. It is formed in front of the lens. |
1. This image is formed by the actual intersection of the reflected or refracted rays. 2. This image is always inverted. 3. This image can be shown on the screen. 4. It formed forward on the mirror. 5. It formed over the lens behind it. |

** ** **
• Why is a convex lens called a convex lens?
Answer :- The rays of light falling on a convex lens meet at a point after refraction. That's why a convex lens is called a virtual lens.

• Why is a concave lens called a diverging lens?
Answer :- Rays of light falling on a concave lens appear scattered from a point after refraction. That's why concave lens is called diverging lens.

Parts of the Lens
1. Principle Axis of Lens
2. Light Centre / Optical Centre
3. Focus of Lens
4. Focus of lens
5. Focal length of lens
6. Radius of Curvature of lens
7. Aperture of lens
** ** ** *
1. Principle Axis of Lens :- The line passing through the center of curvature of the lens is called the principal axis of the lens.

2. Light Centre/Optical Centre:- The light center of a lens is the point located inside it on the principal axis, passing through which the rays of light are refracted without bending.




** ** ** **
👉Click here for numerical questions
The End







